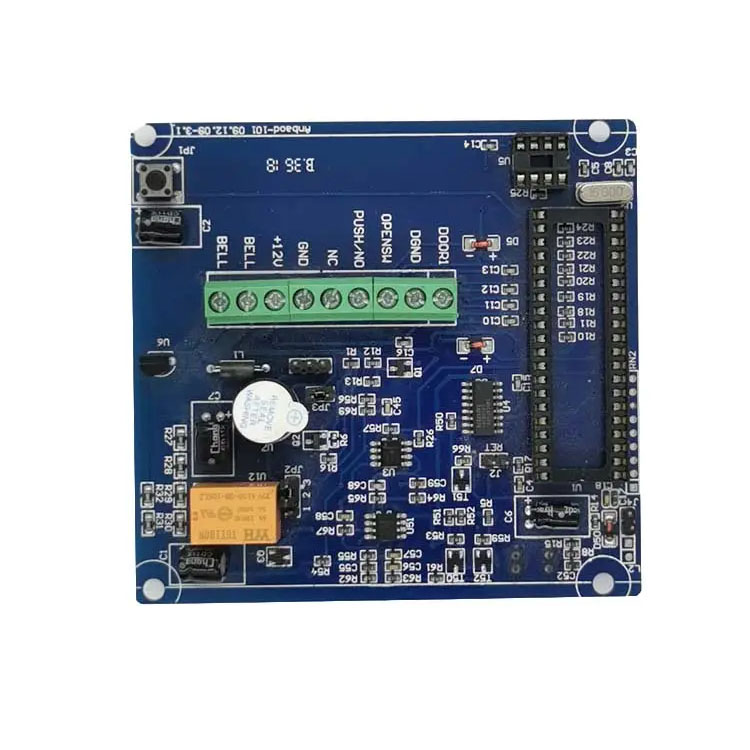
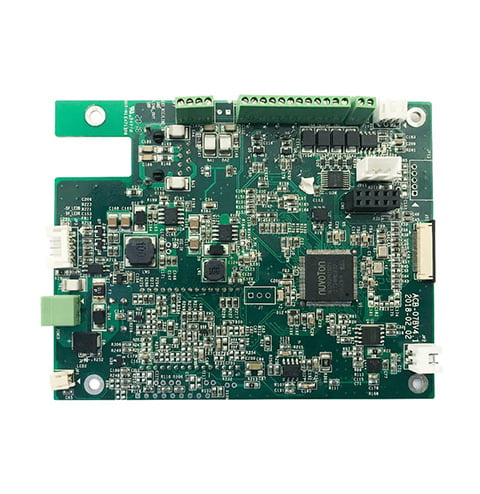
Smt Assembly For Electronic Smart Home
Supplier Type:OEM bluetooth pcba
board thickness:0.2-6mm
Base Material:FR4
Silkscreen Color, Black.white.yellow.red.blue
Number of Layers:1- 40Layers
Testing Service:100% Function Test
Certificate:ISO9001/Iso14001/CE/ROHS
Accuracy of printing:±0.025mm
Components size:0603(Option) L75mm Connector
Pitch:0.15mm
Repeated accuracy:±0.01mm
FOV size:61×45mm
Test speed:9150mm²/Sec
Shootingangle:0-45
Blue Tooth Pcb Smt Circuit Board Electronic Customized
Supplier Type:OEM bluetooth pcba
board thickness:0.2-6mm
Base Material:FR4
Silkscreen Color, Black.white.yellow.red.blue
Number of Layers:1- 40Layers
Testing Service:100% Function Test
Certificate:ISO9001/Iso14001/CE/ROHS
Accuracy of printing:±0.025mm
Components size:0603(Option) L75mm Connector
Pitch:0.15mm
Repeated accuracy:±0.01mm
FOV size:61×45mm
Test speed:9150mm²/Sec
Shootingangle:0-45
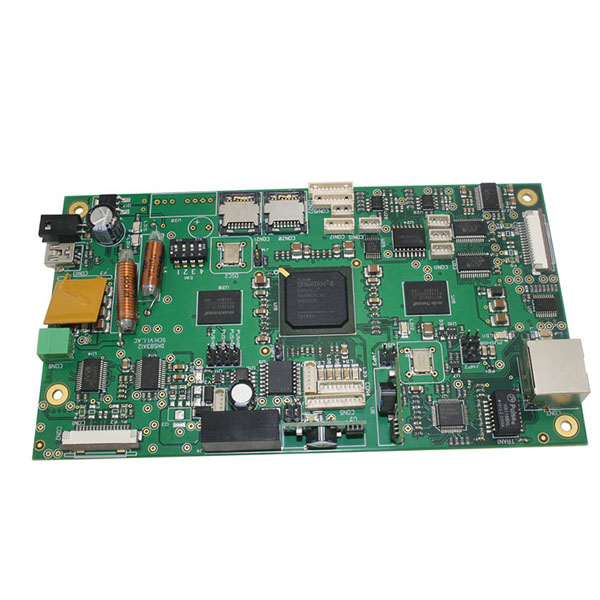

BGA PCB SMT Assembly Electronics PCBA EMS Service
Number of Layer:1,2,4 or 6,upto 18 layer
Order Quantity:1 to 50,000
Board Shape:Retangular,round,slots,cutouts,complex,irregular
Board Type:Rigid, Flexible, Rigid-flexible
Board Material:FR-4 glass epoxy, FR-4 high Tg, Rohs compliant,Aluminum,Rogers,etc.
Board Cutting:Shear,V-score,Tab-routed
Board Thickness:0.2-4.0mm, Flex 0.01-0.25mm
Copper Weight:1.0, 1.5, 2.0 oz
Solder Mask:Double-sided green LPI,Also support Red,White,Yellow,Blue,Black
Silk Screen:Double-sided or single-sided in white,yellow,black,or negative
Silk Screen Min Line Width:0.006” or 0.15mm
Max Board Dimensions:20 inch*20inch or 500mm*500mm
Min Trace/Gap:0.10mm, or 4mils
Min Drill Hole Diameter:0.01”,0.25mm, or 10mils
Surface Finish:HASL,Nickle,Immersion Gold,Immersion Tin,Immersion Silver,OSP,etc.
Board Thickness Tolerance:±10%
Copper Weight Tolerance:± 0.25 oz
Minimal Slot Width:0.12”, 3.0mm, or 120mils
V-Score Depth:20-25% of board thickness
Design File Formate:Gerber RS-274,274D,Eagle and AutoCAD’s DXF,DWG
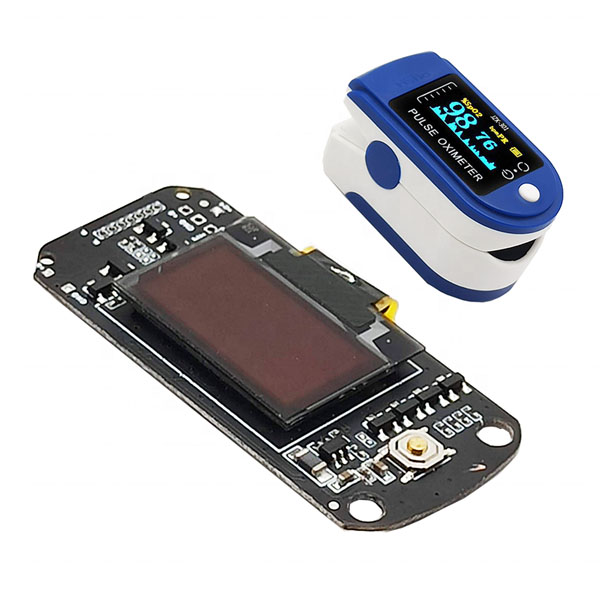

BGA PCB Assembly Factory Manufacture For Pulse Oximeter PCB PCBA one-stop Service
Product Name: PCB Assembly Service
Type: Rigid
Material:FR4, CEM1, CEM3, High Frequency Board,Rogers
Layer:1,2,4,6…20Layer
Shape: Rectangular, Round, Slots, Cutouts, Complex, Irregular
Cutting Shear, V-score, Tab-routed
Board Thickness 0.2-4mm, regular 1.6mm
Copper Thickness:0.5-4oz, regular 1oz
Solder Mask: Green, Red, Blue, Yellow, etc.
Silk Screen: White, Black, etc.
Silk Screen Min Line Width:0.006″ or 0.15mm
Min Trace/Gap:0.1mm or 4mils
Min Drill Hole Diameter 0.01″,0.25mm or 10mils
Surface Finish HASL, ENIG, OSP, etc.
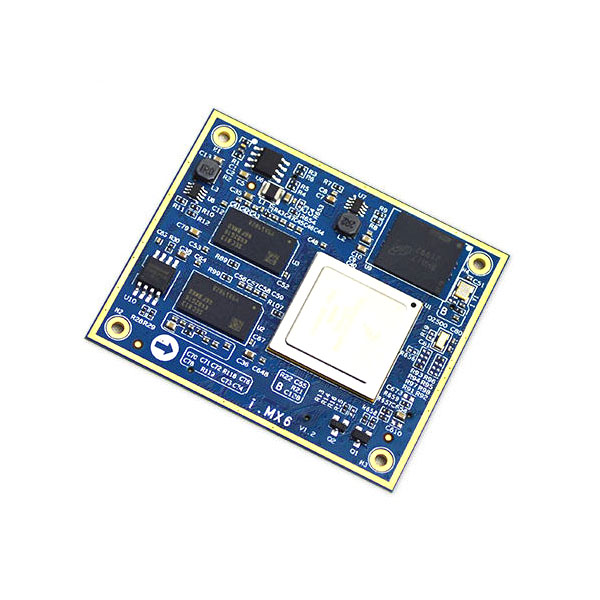
Module ARM Cortex A7 i.MX6 SOM Module BGA Assembly use in IoT Gateway
Name: BGA Assembly
CPU:: ARM Cortex A53 Quad Core 1.28-1.5GHz , MT6739
Operating System: Android 7.0、8.1
Basic Information: GSM 850/900/1800/1900
Screenr: Highest support HD+(1440*720),MIPI interface。
Module Size: 55.5*38.5*3mm
Pin Number: 146pin
Layers: 10 layers ENIG
Flash: 1+8、 2+16、3+32
Wi-Fi: IEEE 802.11 b/g/n, 2.4GHz/5GHz dual-band
GPS: GPS/ GLONASS support AGPS
Bluetooth: BT 4.0、3.0、 2.1 , support BLE
- Description
PCB assembly, or Printed Circuit Board assembly, is the process of mounting and soldering electronic components onto a printed circuit board to create a functional electronic device or circuit. The PCB serves as the foundation for the electrical connections between components, providing a platform for the assembly of various electronic devices, ranging from simple toys to complex computer systems.
The PCB assembly process typically involves several steps:
- Component Placement: Electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits, and connectors, are placed onto the PCB according to the circuit design. This step can be done manually or with the assistance of automated pick-and-place machines, depending on the complexity and volume of the assembly.
- Soldering: Once the components are placed on the PCB, they are soldered onto the board to establish electrical connections. Soldering can be done through wave soldering, reflow soldering, or hand soldering, depending on the specific requirements of the assembly.
- Inspection: After soldering, the assembled PCB undergoes inspection to ensure that all components are properly soldered and positioned according to the design specifications. Various techniques, such as visual inspection, automated optical inspection (AOI), and X-ray inspection, may be used to detect any defects or inconsistencies.
- Testing: Once the inspection is complete, the assembled PCB is tested to verify its functionality and performance. This may involve functional testing, electrical testing, and other tests to ensure that the circuit operates as intended and meets quality standards.
- Final Assembly: After testing, the PCB may undergo additional assembly steps, such as the installation of connectors, switches, and other external components required to complete the electronic device.
Additional types of PCB assembly include:
- Ball Grid Array (BGA) Assembly: BGA is a type of surface mount packaging used for integrated circuits. Instead of pins, BGA packages use solder balls arranged in a grid pattern on the underside of the component.
- Chip-on-Board (COB) Assembly: In COB assembly, bare semiconductor chips are directly mounted onto the PCB substrate and then wire bonded or encapsulated. This method is commonly used in applications where space-saving and cost-efficiency are priorities.
- Flexible PCB Assembly: Flexible PCBs, also known as flex circuits, are made of flexible plastic substrates. Components can be mounted on these substrates using various assembly techniques, including surface mount and through-hole methods.
- Rigid-Flex PCB Assembly): Rigid-flex PCBs combine rigid and flexible substrates into a single board. This allows for more compact and lightweight designs, especially in applications where space is limited or mechanical flexibility is required.
- Wire Harness Assembly: Wire harness assembly involves the integration of wires, cables, and connectors onto the PCB to facilitate interconnection between various electronic components or subsystems. This method is common in complex electronic systems such as automobiles and industrial machinery.
Your outline of the PCB assembly process is quite comprehensive. Here’s a bit more detail on each step:
- Component Procurement: This involves sourcing electronic components from suppliers. It’s crucial to ensure that components are genuine, meet required specifications, and are available in the quantities needed for production.
- Stencil Printing: Solder paste, a mixture of flux and tiny solder particles, is applied onto the PCB through a stencil. The stencil defines where solder paste will be deposited onto the board’s surface, corresponding to the locations where components will be placed.
- Component Placement: Once the solder paste is applied, components are placed onto the PCB. This can be done manually for prototypes or small-volume production, but automated pick-and-place machines are typically used for larger-scale manufacturing. These machines can quickly and accurately position components onto the PCB based on digital design files.
- Soldering: After components are placed, the PCB goes through a soldering process to permanently bond them to the board. There are two main methods for soldering: reflow soldering and wave soldering. Reflow soldering involves heating the entire PCB to melt the solder paste, creating electrical connections. Wave soldering is used primarily for through-hole components, where the PCB is passed over a wave of molten solder.
- Inspection: Once soldering is complete, the assembled PCB undergoes inspection to ensure quality and reliability. This can include visual inspection, automated optical inspection (AOI), or X-ray inspection to detect defects such as solder bridges, insufficient solder joints, or misaligned components.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: After inspection, the assembled PCBs are subjected to functional and electrical tests to verify that they meet performance specifications. This may involve powering up the PCB and running diagnostic tests to ensure proper functionality.
- Packaging and Shipping: Once PCBs pass all quality checks, they are packaged securely to protect them during transportation and storage. Packaging may vary depending on factors such as size, fragility, and shipping requirements. Finally, the assembled PCBs are shipped to customers or other facilities for further integration into larger electronic systems.
These are indeed key benefits of PCB assembly. Here’s a bit more detail on each:
- Increased Efficiency: PCB assembly streamlines the production process by automating repetitive tasks, resulting in higher throughput and lower labor costs. Mass production of electronic circuits becomes feasible, leading to economies of scale and reduced manufacturing lead times.
- High Precision: Automated assembly machines ensure precise component placement with tight tolerances, minimizing the risk of errors that could compromise the functionality or reliability of the final product. This precision is especially crucial for complex circuit designs with densely packed components.
- Better Reliability: Machine assembly processes, coupled with stringent quality control measures, contribute to improved reliability and durability of PCB assemblies. Consistent soldering and inspection techniques help identify and rectify defects early in the manufacturing process, resulting in fewer field failures and warranty claims.
- Space Saving: Surface mount technology (SMT) allows for the mounting of components directly onto the surface of the PCB, eliminating the need for bulky through-holes. This miniaturization enables the design of smaller and more compact electronic devices without compromising functionality, making them ideal for applications where space is limited.
- Flexibility: PCB assembly supports a wide range of component types, sizes, and technologies, offering designers the flexibility to create custom solutions tailored to specific requirements.